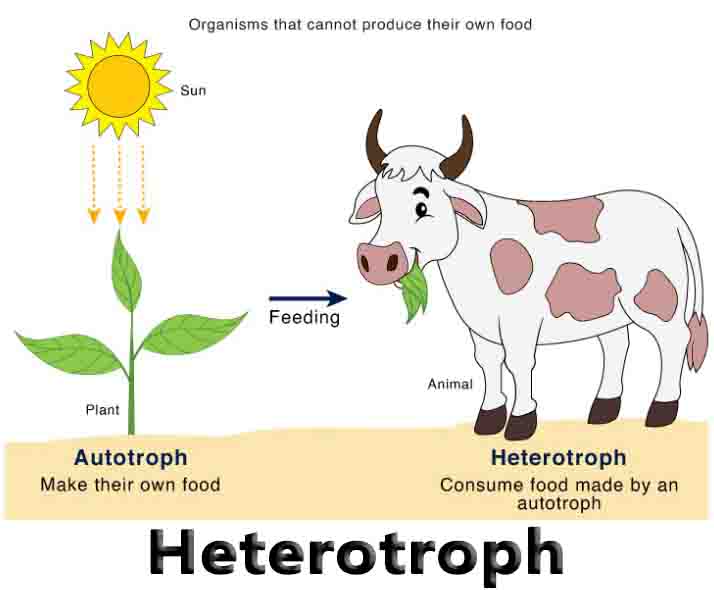
Enzyme Substrate Complex
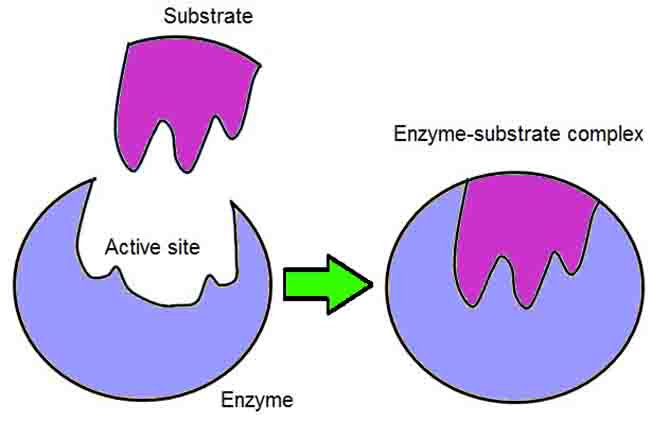
Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition The enzyme substrate complex is a temporary molecule formed when an enzyme comes into perfect contact with its substrate. Without its substrate an enzyme is a slightly different shape. The substrate causes a conformational change, or shape change, when the substrate enters the active site. The active site is the area … Read more